Positioning
Qosium results are tied to time but can also be tied to location.
Qosium supports getting the position of the device in which the Qosium Probe measurement agent runs. When measuring wireless networks, this is valuable information to understand the network quality also in terms of position.
1. Qosium Probe Parameterization #
Qosium Probe supports the following ways to get the position:
- On Linux, if you are using GPSD, Probe can connect directly to the GPSD API for real-time reading of the position.
- If you have a position available elsewhere, e.g., in an external GNSS receiver, you can send the location to Probe using NMEA-0183 (GGA) messages over UDP.
1.1. Activating Position Collection #
Open the QosiumProbe.ini file. It is default located in c:\Program Files\Qosium\ on Windows, /opt/QosiumProbe/bin/ on Linux, and /Applications/QosiumProbe.app/Contents/MacOS/ on macOS.
Find the Positioning parameters section and modify the location_mode value accordingly:
- 3 for GPSD API
- 4 for NMEA messages over UDP. If you want, change the UDP port number for NMEA message reception from the parameter location_nmea_udp_port.
After modifying the ini file, restart Qosium Probe.
2. Manual Position #
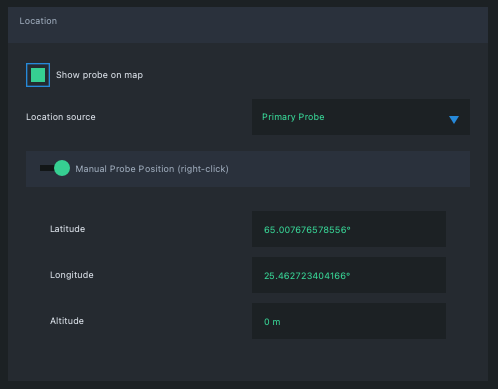
If you desire, you can also set the location manually, even repeatedly. For example, if you are doing indoor mobile measurements but don’t have an indoor positioning system available, manual positioning can do the trick. Give manual position in Qosium Scope as follows:
- On the Map leaf, activate the Manual Probe Position.
- Select Location source according the Probe, Primary or Secondary, you wish to set the location manually.
- Start the measurement.
- Give Probe the position by clicking the right button of your mouse on the map. The position will be shown in the map visualization and stored in the results.